'bitN' N bits (1 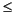
N 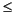
64)'ubitN' N bits (1 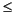
N 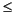
64)| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| fwrite | Examples See Also |
count = fwrite(fid,A,precision) count = fwrite(fid,A,precision,skip)
count = fwrite(fid,A,precision)
writes the elements of matrix A to the specified file, translating MATLAB values to the specified numeric precision. (See "Remarks" for more information.)
The data are written to the file in column order, and a count is kept of the number of elements written successfully. Argument fid is an integer file identifier obtained from fopen.
count = fwrite(fid,A,precision,skip)
includes an optional skip argument that specifies the number of bytes to skip before each precision value is written. With the skip argument present, fwrite skips and writes one value, skips and writes another value, etc. until all of A is written. This is useful for inserting data into noncontiguous fields in fixed-length records. If precision is a bit format like 'bitN' or 'ubitN', skip is specified in bits.
Numeric precisions can differ depending on how numbers are represented in your computer's architecture, as well as by the type of compiler used to produce executable code for your computer.
The tables below give C-compliant, platform-independent numeric precision string formats that you should use whenever you want your code to be portable.
For convenience, MATLAB accepts some C and Fortran data type equivalents for the MATLAB precisions listed. If you are a C or Fortran programmer, you may find it more convenient to use the names of the data types in the language with which you are most familiar.
Two formats map to an input steam of bits rather than bytes:| MATLAB |
C or Fortran |
Interpretation |
|
|
Signed integer; N bits (1 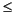 N 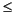 64) |
|
|
Unsigned integer; N bits (1 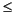 N 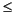 64) |
fid = fopen('magic5.bin','wb');
fwrite(fid,magic(5),'integer*4')
creates a 100-byte binary file, containing the 25 elements of the 5-by-5 magic square, stored as 4-byte integers.
fclose Close one or more open files
ferror Query MATLAB about errors in file input or output
fopen Open a file or obtain information about open files
fprintf Write formatted data to file
fread Read binary data from file
fscanf Read formatted data from file
fseek Set file position indicator
ftell Get file position indicator