| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| fscanf | Examples See Also |
A = fscanf(fid,format) [A,count] = fscanf(fid,format,size)
A = fscanf(fid,format)
reads all the data from the file specified by fid, converts it according to the specified format string, and returns it in matrix A. Argument fid is an integer file identifier obtained from fopen. format is a string specifying the format of the data to be read. See "Remarks" for details.
[A,count] = fscanf(fid,format,size)
reads the amount of data specified by size, converts it according to the specified format string, and returns it along with a count of elements successfully read. size is an argument that determines how much data is read. Valid options are:
fscanf differs from its C language namesakes scanf() and fscanf() in an important respect -- it is vectorized in order to return a matrix argument. The format string is cycled through the file until an end-of-file is reached or the amount of data specified by size is read in.
When MATLAB reads a specified file, it attempts to match the data in the file to the format string. If a match occurs, the data is written into the matrix in column order. If a partial match occurs, only the matching data is written to the matrix, and the read operation stops.
The format string consists of ordinary characters and/or conversion specifications. Conversion specifications indicate the type of data to be matched and involve the character %, optional width fields, and conversion characters, organized as shown below: 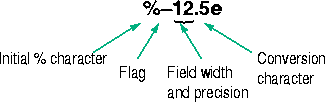
% and the conversion character:%s is used, an element read may use several MATLAB matrix elements, each holding one character. Use %c to read space characters; the format %s skips all white space.
Mixing character and numeric conversion specifications cause the resulting matrix to be numeric and any characters read to appear as their ASCII values, one character per MATLAB matrix element.
For more information about format strings, refer to the scanf() and fscanf() routines in a C language reference manual.
The example in fprintf generates an ASCII text file called exp.txt that looks like:
0.00 1.00000000 0.10 1.10517092 ... 1.00 2.71828183Read this ASCII file back into a two-column MATLAB matrix:
fid = fopen('exp.txt');
a = fscanf(fid,'%g %g',[2 inf]) % It has two rows now.
a = a';
fclose(fid)
fclose Close one or more open files
ferror Query MATLAB about errors in file input or output
fopen Open a file or obtain information about open files
fprintf Write formatted data to file
fread Read binary data from file
fseek Set file position indicator
ftell Get file position indicator
fwrite Write binary data from a MATLAB matrix to a file