| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| fmin | Examples See Also |
Minimize a function of one variable
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2)
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options)
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options,P1,P2, ...)
[x,options] = fmin(...)
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2)
returns a value of x which is a local minimizer of fun(x) in the interval  .
.
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options)
does the same as the above, but uses options control parameters.
x = fmin('fun',x1,x2,options,P1,P2,...)
fun(x,P1,P2,...). Pass an empty matrix for options to use the default value.
[x,options] = fmin(...)
returns, in options(10), a count of the number of steps taken.
fmin('cos',3,4) computes  to a few decimal places.
to a few decimal places.
fmin('cos',3,4,[1,1.e-12]) displays the steps taken to compute  to 12 decimal places.
To find the minimum of the function
to 12 decimal places.
To find the minimum of the function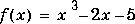 on the interval (0
on the interval (0,2), write an M-file called f.m.
function y = f(x) y = x.^3-2*x-5;Then invoke
fmin with
x = fmin('f', 0, 2)
The result is
x =
0.8165
The value of the function at the minimum is
y = f(x)
y =
-6.0887
The algorithm is based on golden section search and parabolic interpolation. A Fortran program implementing the same algorithms is given in [1].
fmins Minimize a function of several variables
fzero Zero of a function of one variable
foptions in the Optimization Toolbox (or type help foptions).