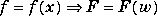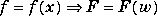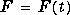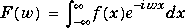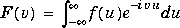Fourier integral transform.
Syntax
F = fourier(f)
F = fourier(f,v)
F = fourier(f,u,v)
Description
F = fourier(f) is the Fourier transform of the symbolic scalar f with default independent variable x. The default return is a function of w. The Fourier transform is applied to a function of x and returns a function of w.
If f = f(w), fourier returns a function of t.
By definition
where x is the symbolic variable in f as determined by findsym.
F = fourier(f,v) makes F a function of the symbol v instead of the default w.
F = fourier(f,u,v) makes f a function of u and F a function of v instead of the default variables x and w, respectively.
Examples
Fourier Transform |
MATLAB Command |
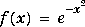
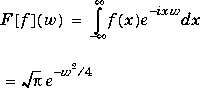
|
f = exp(-x^2)
fourier(f)returns
pi^(1/2)*exp(-1/4*w^2)
|
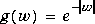
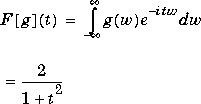
|
g = exp(-abs(w))
fourier(g)
returns 2/(1+t^2)
|
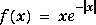
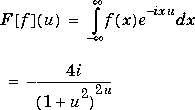
|
f = x*exp(-abs(x))
fourier(f,u)
returns -4*i/(1+u^2)^2*u
|

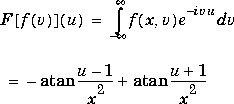
|
syms x real
f = exp(-x^2*abs(v))*sin(v)/v
fourier(f,v,u)
returns -atan((u-1)/x^2)+atan((u+1)/x^2)
|
See Also
ifourier, laplace, ztrans
[ Previous | Help Desk | Next ]