| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| roots | Examples See Also |
r = roots(c)
r = roots(c)
c.
Row vector c contains the coefficients of a polynomial, ordered in descending powers. If c has n+1 components, the polynomial it represents is 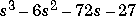 .
Note the relationship of this function to
.
Note the relationship of this function to p = poly(r), which returns a row vector whose elements are the coefficients of the polynomial. For vectors, roots and poly are inverse functions of each other, up to ordering, scaling, and roundoff error.
The polynomial  is represented in MATLAB as
is represented in MATLAB as
p = [1 -6 -72 -27]
r = roots(p)
r =
12.1229
-5.7345
-0.3884
The algorithm simply involves computing the eigenvalues of the companion matrix:
A = diag(ones(n-2,1),-1); A(1,:) = -c(2:n-1)./c(1); eig(A)It is possible to prove that the results produced are the exact eigenvalues of a matrix within roundoff error of the companion matrix
A, but this does not mean that they are the exact roots of a polynomial with coefficients within roundoff error of those in c.
fzero Zero of a function of one variable
poly Polynomial with specified roots
residue Convert between partial fraction expansion and polynomial
coefficients