| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| log2 | Examples See Also |
Base 2 logarithm and dissect floating-point numbers into exponent and mantissa
Y =log2(X) [F,E]=log2(X)
Y = log2(X)
computes the base 2 logarithm of the elements of X.
[F,E] = log2(X)
returns arrays F and E. Argument F is an array of real values, usually in the range 0.5 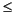
abs(F) < 1. For real X, F satisfies the equation: X = F.*2.^E. Argument E is an array of integers that, for real X, satisfy the equation: X = F.*2.^E.
This function corresponds to the ANSI C function frexp() and the IEEE floating-point standard function logb(). Any zeros in X produce F = 0 and E = 0.
For IEEE arithmetic, the statement [F,E] = log2(X) yields the values: |
X
|
F
|
E
|
1 |
1/2 |
1 |
pi |
pi/4 |
2 |
-3 |
-3/4 |
2 |
eps |
1/2 |
-51 |
realmax |
1-eps/2 |
1024 |
realmin |
1/2 |
-1021 |
log Natural logarithm
pow2 Base 2 power and scale floating-point numbers