| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| besselh |
Bessel functions of the third kind (Hankel functions)
H = besselh(nu,K,Z) H = besselh(nu,Z) H = besselh(nu,1,Z,1) H = besselh(nu,2,Z,1) [H,ierr] = besselh(...)The differential equation
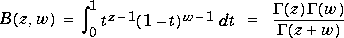
 is a nonnegative constant, is called Bessel's equation, and its solutions are known as Bessel functions.
is a nonnegative constant, is called Bessel's equation, and its solutions are known as Bessel functions. 
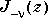 form a fundamental set of solutions of Bessel's equation for noninteger
form a fundamental set of solutions of Bessel's equation for noninteger  .
.  is a second solution of Bessel's equation--linearly independent of
is a second solution of Bessel's equation--linearly independent of  -- defined by:
-- defined by: The relationship between the Hankel and Bessel functions is:
The relationship between the Hankel and Bessel functions is:
H = besselh(nu,K,Z)
for K = 1 or 2 computes the Hankel functions
 or
or 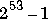 for each element of the complex array
for each element of the complex array Z. If nu and Z are arrays of the same size, the result is also that size. If either input is a scalar, it is expanded to the other input's size. If one input is a row vector and the other is a column vector, the result is a two-dimensional table of function values.
H = besselh(nu,Z)
uses K = 1.
H = besselh(nu,1,Z,1)
scales 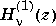 by
by exp(-i*z).
H = besselh(nu,2,Z,1)
scales 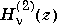 by
by exp(+i*z).
[H,ierr] = besselh(...)
also returns an array of error flags: