| Symbolic Math Toolbox | Search Help Desk | |
| taylor | Examples | See Also |
r = taylor(f) r = taylor(f,n,v) r = taylor(f,n,v,a)
taylor(f,n,v) returns the (n-1)-order Maclaurin polynomial approximation to f, where f is a symbolic expression representing a function and v specifies the independent variable in the expression. v can be a string or symbolic variable.
taylor(f,n,v,a) returns the Taylor series approximation to f about a. The argument a can be a numeric value, a symbol, or a string representing a numeric value or an unknown.
You can supply the arguments n, v, and a in any order. taylor determines the purpose of the arguments from their position and type.
You can also omit any of the arguments n, v, and a. If you do not specify v, taylor uses findsym to determine the function's independent variable. n defaults to 6.
The Taylor series for an analytic function f(x) about the basepoint x=a is given below.
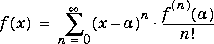
taylor command and its relation to Taylor and MacLaurin series.f is a function of two or more variables (f=f(x,y,...)), there is a fourth parameter that allows you to select the variable for the Taylor expansion. Look at this table for illustrations of this feature.findsym