Sine and hyperbolic sine
Syntax
Y = sin(X)
Y = sinh(X)
Description
The sin and sinh commands operate element-wise on arrays. The functions' domains and ranges include complex values. All angles are in radians.
Y = sin(X)
returns the circular sine of the elements of X.
Y = sinh(X)
returns the hyperbolic sine of the elements of X.
Examples
Graph the sine function over the domain 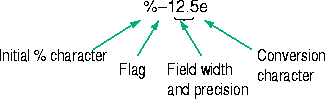 and the hyperbolic sine function over the domain
and the hyperbolic sine function over the domain 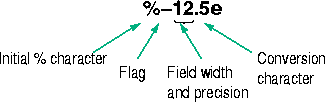
x = -pi:0.01:pi; plot(x,sin(x))
x =
The expression sin(pi) is not exactly zero, but rather a value the size of the floating-point accuracy eps, because pi is only a floating-point approximation to the exact value of  .
.
Algorithm

See Also
asin, asinh Inverse sine and inverse hyperbolic sine
[ Previous | Help Desk | Next ]
 and the hyperbolic sine function over the domain
and the hyperbolic sine function over the domain 
 .
.
