| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| rand | Examples See Also |
Uniformly distributed random numbers and arrays
Y = rand(n)
Y = rand(m,n)
Y = rand([m n])
Y = rand(m,n,p,...)
Y = rand([m n p...])
Y = rand(size(A))
rand
s = rand('state')
The rand function generates arrays of random numbers whose elements are uniformly distributed in the interval (0,1).
Y = rand(n)
returns an n-by-n matrix of random entries. An error message appears if n is not a scalar.
Y = rand(m,n) or Y = rand([m n])
returns an m-by-n matrix of random entries.
Y = rand(m,n,p,...) or Y = rand([m n p...])
generates random arrays.
Y = rand(size(A))
returns an array of random entries that is the same size as A.
rand,
s = rand('state')
returns a 35-element vector containing the current state of the uniform generator. To change the state of the generator: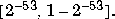 Theoretically, it can generate over
Theoretically, it can generate over  values before repeating itself. MATLAB 4 used random number generators with a single seed.
values before repeating itself. MATLAB 4 used random number generators with a single seed. rand('seed',0)and rand('seed',j) use the MATLAB 4 generator. rand('seed') returns the current seed of the MATLAB 4 uniform generator. rand('state',j) and rand('state',s) use the MATLAB 5 generator.
R = rand(3,4) may produce
R =
0.2190 0.6793 0.5194 0.0535
0.0470 0.9347 0.8310 0.5297
0.6789 0.3835 0.0346 0.6711
This code makes a random choice between two equally probable alternatives.
if rand < .5
'heads'
else
'tails'
end
randn Normally distributed random numbers and arrays
randperm Random permutation
sprand Sparse uniformly distributed random matrix
sprandn Sparse normally distributed random matrix