| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| ndgrid | Examples See Also |
Generate arrays for multidimensional functions and interpolation
[X1,X2,X3,...] = ndgrid(x1,x2,x3,...) [X1,X2,...] = ndgrid(x)
[X1,X2,X3,...] = ndgrid(x1,x2,x3,...)
transforms the domain specified by vectors x1,x2,x3... into arrays X1,X2,X3... that can be used for the evaluation of functions of multiple variables and multidimensional interpolation. The ith dimension of the output array Xi are copies of elements of the vector xi.
[X1,X2,...] = ndgrid(x)
is the same as [X1,X2,...] = ndgrid(x,x,...).
To evaluate the function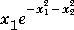 over the range
over the range  ;
;  :
:
[X1,X2] = ndgrid(-2:.2:2, -2:.2:2); Z = X1 .* exp(-X1.^2 - X2.^2); mesh(Z)The
ndgrid function is like meshgrid except that the order of the first two input arguments are switched. That is, the statement
[X1,X2,X3] = ndgrid(x1,x2,x3)
[X2,X1,X3] = meshgrid(x2,x1,x3).
ndgrid is better suited to multidimensional problems that aren't spatially based, while meshgrid is better suited to problems in two- or three-dimensional Cartesian space.
meshgrid Generate X and Y matrices for three-dimensional plots
interpn Multidimensional data interpolation (table lookup).