Construct an inline object
Syntax
g = inline(expr)
g = inline(expr,arg1,arg2, ...)
g = inline(expr,n)
Description
inline(expr)
expr. The input argument to the inline
function is automatically determined by searching expr for an isolated lower
case alphabetic character, other than i or j, that is not part of a word formed
from several alphabetic characters. If no such character exists, x is used. If the
character is not unique, the one closest to x is used. If there is a tie, the one
later in the alphabet is chosen.
inline(expr,arg1,arg2, ...)
arg1, arg2,.... Multicharacter symbol names may be used.
inline(expr,n), where n is a scalar, constructs an inline function whose input arguments are x, P1, P2, ...
Remarks
Three commands related to inline allow you to examine an inline function object and determine how it was created.
char(fun) converts the inline function into a character array. This is identical to formula(fun).
argnames(fun) returns the names of the input arguments of the inline object fun as a cell array of strings.
formula(fun) returns the formula for the inline object fun.
A fourth command vectorize(fun) inserts a . before any ^, * or /' in the formula for fun. The result is a vectorized version of the inline function.
Examples
Create a simple inline function to square a number:
g = inline('t^2')
g =
Inline function:
g(t) = t^2
char(g)
ans =
t^2
Create an inline function to compute the formula 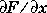 :
:
g = inline('3*sin(2*x.^2)')
g =
Inline function:
g(x) = 3*sin(2*x.^2)
argnames(g)
ans =
'x'
formula(g)
ans =
3*sin(2*x.^2)
g(pi)
ans =
2.3306
g(2*pi)
ans =
-1.2151
fmin(g,pi,2*pi)
ans =
3.8630
[ Previous | Help Desk | Next ]
 :
: