| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| filter | See Also |
Filter data with an infinite impulse response (IIR) or finite impulse response (FIR) filter
y = filter(b,a,X) [y,zf] = filter(b,a,X) [y,zf] = filter(b,a,X,zi) y = filter(b,a,X,zi,dim) [...] = filter(b,a,X,[],dim)The
filter function filters a data sequence using a digital filter which works for both real and complex inputs. The filter is a direct form II transposed implementation of the standard difference equation (see "Algorithm").
y = filter(b,a,X)
filters the data in vector X with the filter described by numerator coefficient vector b and denominator coefficient vector a. If a(1) is not equal to 1, filter normalizes the filter coefficients by a(1). If a(1) equals 0, filter returns an error.
If X is a matrix, filter operates on the columns of X. If X is a multidimensional array, filter operates on the first nonsingleton dimension.
[y,zf] = filter(b,a,X)
returns the final conditions, zf, of the filter delays. Output zf is a vector of max(size(a),size(b)) or an array of such vectors, one for each column of X.
[y,zf] = filter(b,a,X,zi)
accepts initial conditions and returns the final conditions, zi and zf respectively, of the filter delays. Input zi is a vector (or an array of vectors) of length max(length(a),length(b))-1.
y = filter(b,a,X,zi,dim)
and
[...] = filter(b,a,X,[],dim)
operate across the dimension dim.
The filter function is implemented as a direct form II transposed structure,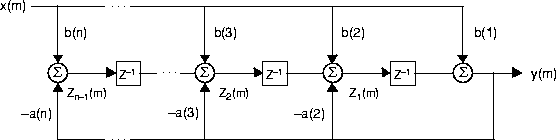
y(n) = b(1)*x(n) + b(2)*x(n-1) + ... + b(nb+1)*x(n-nb)
- a(2)*y(n-1) - ... - a(na+1)*y(n-na)
where n-1 is the filter order, and which handles both FIR and IIR filters [1].
The operation of filter at sample m is given by the time domain difference equations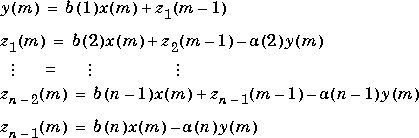
filter2 Two-dimensional digital filtering
[1] Oppenheim, A. V. and R.W. Schafer. Discrete-Time Signal Processing, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989, pp. 311-312.