| MATLAB Function Reference | Search Help Desk |
| cov | Examples See Also |
C = cov(X) C = cov(x,y)
C = cov(x)
where x is a vector returns the variance of the vector elements. For matrices where each row is an observation and each column a variable, cov(x) is the covariance matrix. diag(cov(x)) is a vector of variances for each column, and sqrt(diag(cov(x))) is a vector of standard deviations.
C = cov(x,y),
where x and y are column vectors of equal length, is equivalent to cov([x y]).
cov removes the mean from each column before calculating the result.
The covariance function is defined as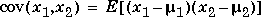
A = [-1 1 2 ; -2 3 1 ; 4 0 3]. To obtain a vector of variances for each column of A:
v = diag(cov(A))'
v =
10.3333 2.3333 1.0000
v with covariance matrix C:
C =
10.3333 -4.1667 3.0000
-4.1667 2.3333 -1.5000
3.0000 -1.5000 1.0000
The diagonal elements C(i,i) represent the variances for the columns of A. The off-diagonal elements C(i,j) represent the covariances of columns i and j.
xcorr, xcov in the Signal Processing Toolbox, and:
corrcoef Correlation coefficients
mean Average or mean value of arrays
std Standard deviation